Understanding Load balancers - How Presear Softwares can help in scaling up your software application
This Post is going to be about Load Balancers and the way requests are dealt with the usage of Load Balancer.
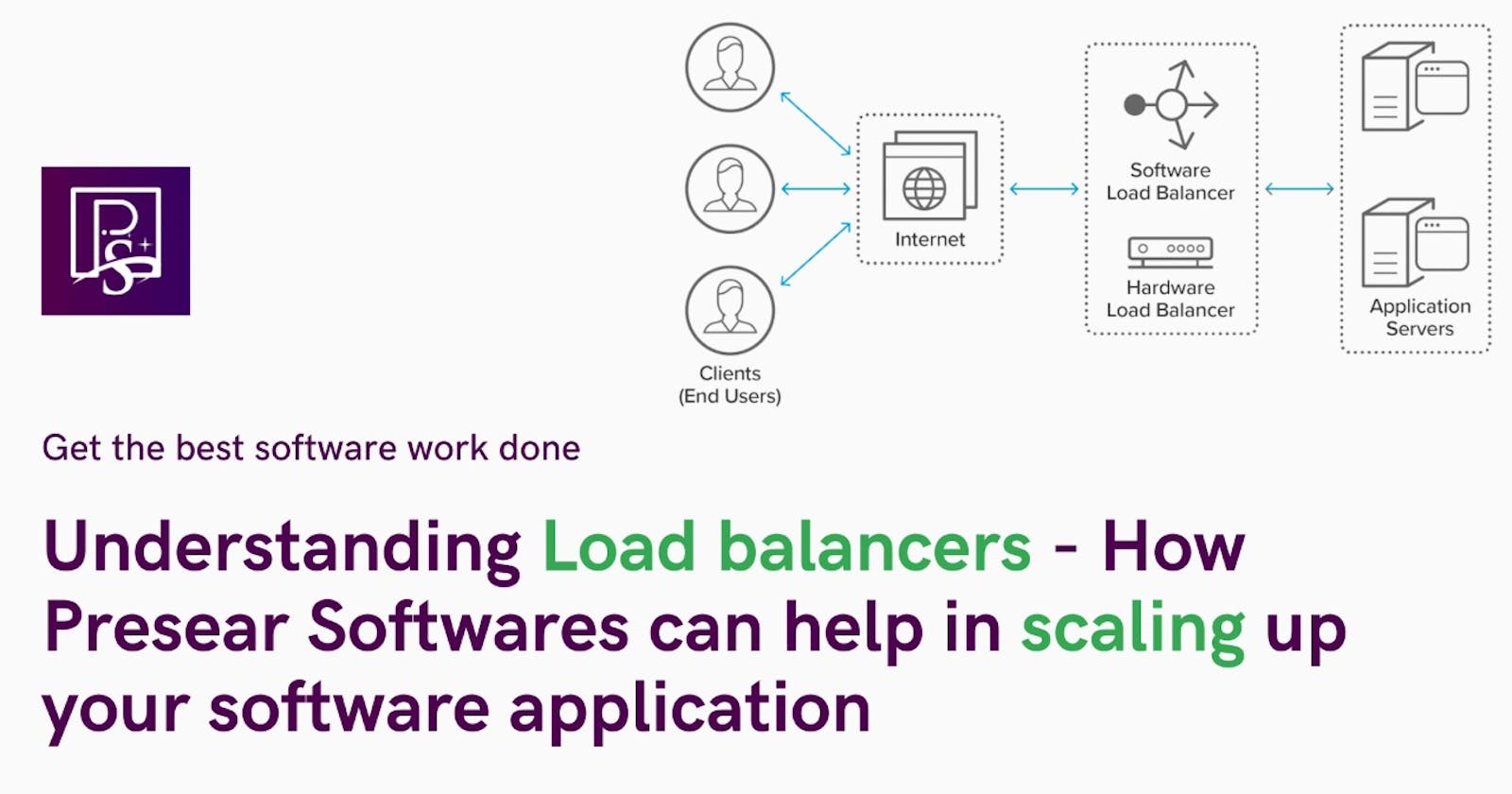
What is Load Balancer
It is a device which allows all of the client's request to be distributed to the backend server i.e. it balances the loads. It's work is to equally distribute the load to the backend clusters which guarantees ideal overall performance of usual application.
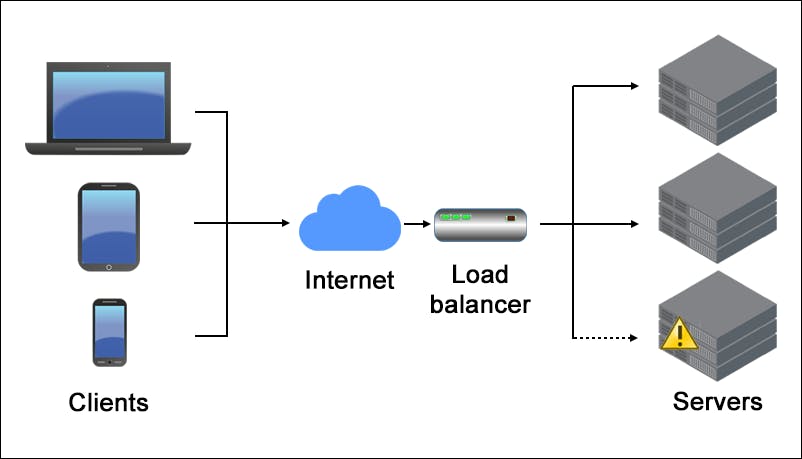
Benefits of Cloud Load-balancing
High-availability: While multiple servers are put together into practice, it boosts availability.
Scalability: Unusual traffic spikes can affect server performance, however load-balancing offers the functionality to feature greater servers to the group to control the developing incoming requests.
Flexibility: Maintenance of work is easy because administrators can direct all traffic to one server and place the other load balancer in active/passive mode. This allows them to do the maintenance without causing downtime issue.
Economical: Cloud load-balancers are low-budget because the price is primarily based totally on the quantity of aid used, that's the 'pay-as-you-go' model.
General Load Balancer Types
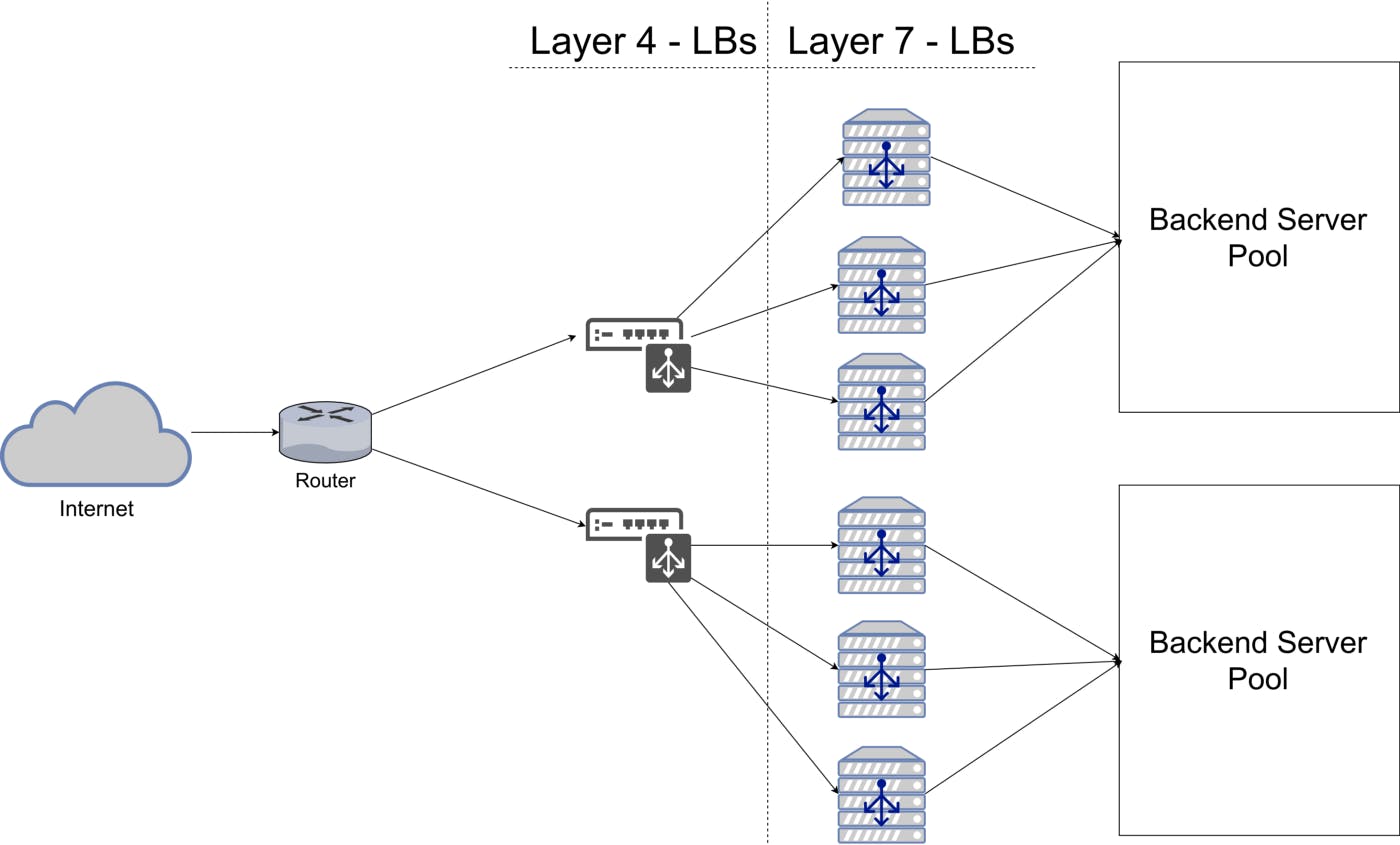
Layer7(Application Layer) - Layer 4 load balancer operates at the transport level, manages traffic based on network information such as application ports without seeing the actual content of messages.
Layer4(Transport Layer) - Layer 7 load balancer operates at the application level, using protocols such as HTTP, HTTPs and Web Socket to make decisions based on the actual content of each message. A Layer 7 load balancer terminates network traffic, performs decryption as needed, inspects messages, makes content-based routing decisions.
 source
sourceMost Common Load Balancing Algorithms
- Round Robin
- Least Connection
- Least Response Time
- Least Bandwidth
- Hashing
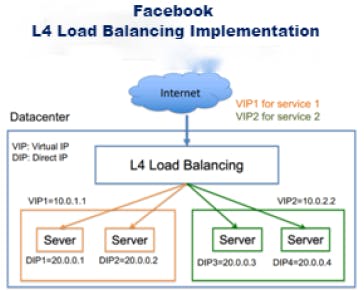
How do big Companies handles large number of requests?
They uses lots and lots of load balancers. Once a request is made very efficient and highly scalable load balancers direct the requests to a very large number of frontend webservers. Many machines are servicing a single request. The frontend webservers do very little of the work involved in actually servicing a request. They are mostly for HTTP parsing and routing to more tiers of servers, each cluster of which does a very small and specialized part of the larger task of generating a page.
Below is the instance of facebook(meta) usage of load balancer
How Presear Softwares can help scaling your application ?
Presear Softwares has expertise in system design and especially scaling by using efficient cloud architecture. We have in house cloud developers who can fit load balancers properly with automatic upscaling and downscaling features. This load balancing will improvise your software in the following way,
- Requests per second increases by 10,000
- Simultaneous connections increases by 10,000
- New SSL connections per second increase by 250
The load balancers used by Presear Softwares are better than others because,
- Our Load Balancers are monitored for availability. If any anomalies are detected, our systems will correct them and fix them. Your Load Balancer will continue running smoothly without any extra work from you.
- Load Balancers automatically provision and renew SSL certificates free of charge through Let’s Encrypt. Load Balancers also support HTTP/2, providing better performance for your users.
- Automatically pass a client’s IP address and port through to your server
- Get more flexibility—resize your Load Balancer when you need to and scale your apps with ease.
- Supports Kubernetes
For understanding how Presear Softwares can help you more feel free to mail us your project idea or the problem statement at support@presear.com
Conclusion
Load Balancers are what they declare to be, a resource intended for dispensing the workload(requests) among the internet servers to deal with HTTP requests.
It lets you evenly distribute network traffic across multiple servers in a server farm to prevent failure caused by overloading a particular resource. This strategy improves the performance and availability of applications, websites, databases, and other computing resources. It also helps process user requests quickly and accurately.